Accurately tracking conversions helps us understand human behaviour and optimize business strategies. The reliability of this data is what helps businesses make informed decisions about their products and services. But, duplicate conversions can generate a lot of false data that leads to skewed insights.
Before the Google Analytics 4 (GA4) guidelines, SEO experts used some creative ways to avoid duplicate conversions. But, in GA4, conversions are a type of event that may get triggered multiple times in a session.
Let’s explore how to track conversions precisely and maximize GA4’s benefits.
Managing Conversions in GA4
In Universal Analytics, if a user completes the same goal multiple times during the same session, it is counted only once. But, in GA4, if a user submits three forms during a session, it is counted as three conversions.
There are some effective ways of making GA4 track your conversions accurately. Here are the most commonly used ones:
Avoiding Double-Counting
Double counting occurs when the same user action is counted as multiple separate conversions. This can be countered by creating a custom event and tracking that instead.
GA4 offers a feature called Audience Triggers. When a user enters an ‘audience,’ GA4 will trigger an event. This event can then be marked as a conversion.
With recent updates, GA4 offers a built-in feature where you can set how counting will be done. In the Conversions section, change the counting method to “Once per session.”
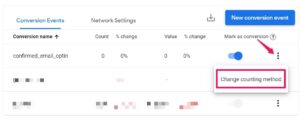
Google Analytics Audience Constraints
Audience Triggers are a great way of avoiding duplicate conversions. But websites use other conversion trackers as well. These conversion trackers may be susceptible to double-counting.
Facebook and Google GA4 use precise transaction ID matching to eliminate double-counting. But, some smaller trackers may need to be configured to avoid this issue.
One way to do that is by using a Tag Manager. We will introduce the Google Tag Manager’s features and benefits later in this blog.
Making a Conversion Funnel
A conversion funnel is a list of steps that users usually take before completing a process (like registering themselves on a website).
For example, a GA4 funnel might have the following steps:
- Session_start
Indirectly followed by
- Visiting our event_page
Indirectly followed by
- Landing on the Thank You page/Conversion
This funnel could lead to three possibilities:
- Users go through the event page and then convert.
- Users go through a different sponsorship page and then convert.
- Users go to the event page, then the sponsorship page, and then convert.
The third possibility could lead to double-counting. This is a common pitfall of using conversion funnels.
The Issue with “directly followed by”
To rectify the above situation, changing “indirectly followed by” to “directly followed by” is not the most viable solution.
When “directly followed by” is used, GA4 tracks all random user actions between the two events. If a user scrolls from the sponsorship page to the thank you page, then the scrolling is tracked as an event. This disrupts the funnel of actions.
What about “within x minutes”?
The new GA4 features also allow us to set up a timer. This timer tracks all events between the funnel-listed steps taken by a user.
For example, it can track users who visited the landing page and then came back to convert a few days later. Or the time taken for a user to convert after landing on the event page.
Despite being relevant insights, these do not track legitimate conversions.
Alternatives
GA4 features offer many benefits and new tools to use. But, when it comes to tracking your conversions, Google Tag Manager can work wonders.
Let’s dive into how Google Tag Manager can help SEO experts track conversions more accurately.
Managing Conversions in Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is an excellent alternative method for tracking conversions on your website. But you will have to run all of your tracking via Tag Manager.
Tag Manager offers the following advantages:
- Makes sure that all tracking tags are operating similarly.
- Offers more control over the various paths to conversion.
Avoiding Double-Counting
In the Google Tag Manager, we can use cookies to eliminate the risk of double-counting.
- Whenever a user converts, a cookie is set with that event for that particular user.
- The cookie disappears after a set period of inactivity (usually 30 minutes).
- If the user tries to trigger another conversion, the presence of the cookie is checked first. If the cookie is still there, then the conversion is not registered.
Cookie Setting in JavaScript
Setting a cookie in JavaScript may seem more tedious than using GA4 to track conversions, but it is well worth the effort.
All you have to do is:
- Create a JavaScript code that notes the current time and creates a cookie to track it.
- Then, add a trigger on all pages that fires when a user is on it.
Reading the Value of Our Cookie
The cookie values can be automatically read by the Tag Manager in the variables section. You can create a new variable and cookie in that section.
It will show up in the variables list. This value (true or false) is then used to fire triggers on a certain event(s).
Setting a Cookie When Someone Converts
So when a trigger is fired based on the set event, the tag you set will send the conversion information (i.e., it will check if a cookie already exists for that user).
But you need to make sure that the cookie is set when a user has not converted. If they have, then a trigger should reset the cookie.
Refreshing the Cookie
If a user has already converted and initiated a conversion event again, then no tag should fire. To ensure that, you will need to add a ‘refresh’ trigger tag to the cookie. Remember the following points, however:
- When someone converts, they get a “converted” cookie for the next 30 minutes.
- With each page load, the cookie should also reset for another 30 minutes.
- If the user does not load any page for 30 minutes, then the cookie should expire (so that the ‘refresh’ trigger does not fire).
Strange Conversions Without Page Visits
Sometimes, users save or bookmark a “thank you” page and keep coming back to it. This can lead to false conversions where users frequently visit the final event pages.
To counter this, you can create a conversion funnel.
- This funnel will have a list of certain pages that a user must pass through in order to convert.
- Then, you can create a cookie to track the pages that a user visits.
- If the user passes through one of the funnel pages or if their last visited page leads to the “thank you” page, then the cookie can count it as a conversion.
GA4 Conversion Best Practices
Data analysis for most websites relies heavily on conversion management. It is vital, therefore, that you update your website to track GA4 conversions.
The Google Tag Manager is also an efficient tool for managing tags and streamlining conversion tracking. Armed with these strategies, you can easily pave a path to better, data-driven decisions.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
0 / 5. 0